Tick-borne diseases are on the rise due to expanding tick populations caused by climate change, habitat changes, and increased outdoor activity. Warmer winters and longer active seasons help ticks survive and spread into new areas, raising the risk of illnesses like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Recognizing symptoms, practicing prevention, and staying informed about ecological shifts are key. Discover more ways to protect yourself from this growing health threat as you explore further.
Key Takeaways
- Climate change and habitat expansion increase tick populations and extend active seasons, raising disease transmission risks.
- Warmer winters and ecological shifts facilitate tick survival in new regions, contributing to rising tick-borne disease cases.
- Increased outdoor activity and habitat disturbance heighten human exposure to infected ticks.
- Advances in diagnostics and vaccines improve early detection and prevention of tick-borne illnesses.
- Community education and preventative measures are essential to combat the growing prevalence of tick-borne diseases.
Understanding the Different Types of Tick-Borne Diseases

Understanding the different types of tick-borne diseases is essential because these illnesses can vary greatly in symptoms and severity. Different tick species are responsible for transmitting specific diseases, which influences how you might experience symptoms. For example, Lyme disease is commonly spread by black-legged ticks, while Rocky Mountain spotted fever comes from American dog ticks or rocky mountain ticks. Disease transmission occurs when a tick bites and feeds on you, transferring pathogens into your bloodstream. Not all ticks carry diseases, but the risk increases with certain tick species. Recognizing which tick species are involved helps you understand potential health risks and prompts timely actions like removal and seeking medical attention if symptoms develop. Knowing these distinctions is key to early detection and prevention.
Factors Contributing to the Increase in Tick Populations

Warmer winters mean ticks have longer seasons to feed and reproduce, boosting their numbers. As habitats expand into new areas, more wildlife and humans become exposed to these pests. Understanding these factors helps explain why tick populations are growing rapidly.
Warmer Winters Extend Seasons
As winters become milder, tick populations can survive and thrive for longer periods each year. This shift affects tick ecology and disrupts typical seasonal patterns. You’ll notice that ticks remain active well beyond their usual dormant months, increasing the risk of bites and disease transmission. Here’s how warmer winters impact tick activity: 1. They extend the active season, giving ticks more time to find hosts. 2. They disrupt traditional seasonal patterns, making ticks active earlier and later in the year. 3. They support higher survival rates, leading to larger tick populations overall. 4. Incorporating temperature regulation strategies can help manage tick activity levels and reduce exposure risks. Additionally, understanding the ecological impacts of climate change helps predict future trends in tick distribution and disease spread. The changing climate also influences vector ecology, which can lead to shifts in where and when ticks are most prevalent. These ecological changes can alter habitat suitability for ticks, further expanding their range. With longer active periods, you’ll find ticks more prevalent in outdoor activities year-round. Understanding these changes helps you better protect yourself from tick bites and associated diseases.
Expanding Wildlife Habitats
Expanding wildlife habitats due to human development and environmental changes create more opportunities for ticks to find hosts. As forests and grasslands grow or reconnect through wildlife corridors, animals like deer and rodents thrive, increasing tick populations. Habitat fragmentation, caused by roads and urbanization, pushes animals into smaller, concentrated areas, making it easier for ticks to attach. Wildlife corridors enable animals to migrate more freely, spreading ticks over larger areas and introducing them to new environments. These changes support the growth of tick populations by providing abundant hosts and suitable environments. Additionally, portable camping gear often takes place in areas with expanding wildlife habitats, increasing human exposure to ticks. As the environment adapts and changes, the ecological balance shifts, further encouraging the spread of ticks and the diseases they carry. The presence of reservoir hosts, such as rodents and birds, amplifies the transmission cycle of tick-borne pathogens. This interconnected system of wildlife and environmental factors highlights how habitat connectivity can influence disease dynamics. Consequently, as wildlife habitats expand and become more connected, the risk of tick-borne disease transmission rises, affecting both humans and animals.
Recognizing Symptoms and Diagnosing Tick-Borne Illnesses

Recognizing the symptoms of tick-borne illnesses can be challenging because they often resemble those of other infections. Building symptoms awareness helps you catch issues early. Common signs include fever, fatigue, and skin rashes. To improve diagnosis, healthcare providers use various diagnostic methods, such as:
- Blood tests to detect specific antibodies or pathogens
- Physical exams noting telltale rash patterns
- Patient history, including recent outdoor activities
- Understanding the importance of indoor air quality in overall health, as poor air quality can exacerbate symptoms or complicate recovery. Additionally, considering environmental factors like home decor elements can influence comfort and stress levels, indirectly affecting health outcomes. Recognizing environmental influences on health can also help in managing and preventing tick-borne illnesses. Being attentive to symptom changes and recent tick exposure is essential. Early diagnosis allows for prompt treatment, reducing complications. Remember, symptoms may vary depending on the illness, so a combination of symptoms awareness and proper diagnostic methods is vital for accurate identification. Don’t delay seeking medical advice if you notice signs after potential exposure.
Prevention Strategies to Minimize Tick Bites
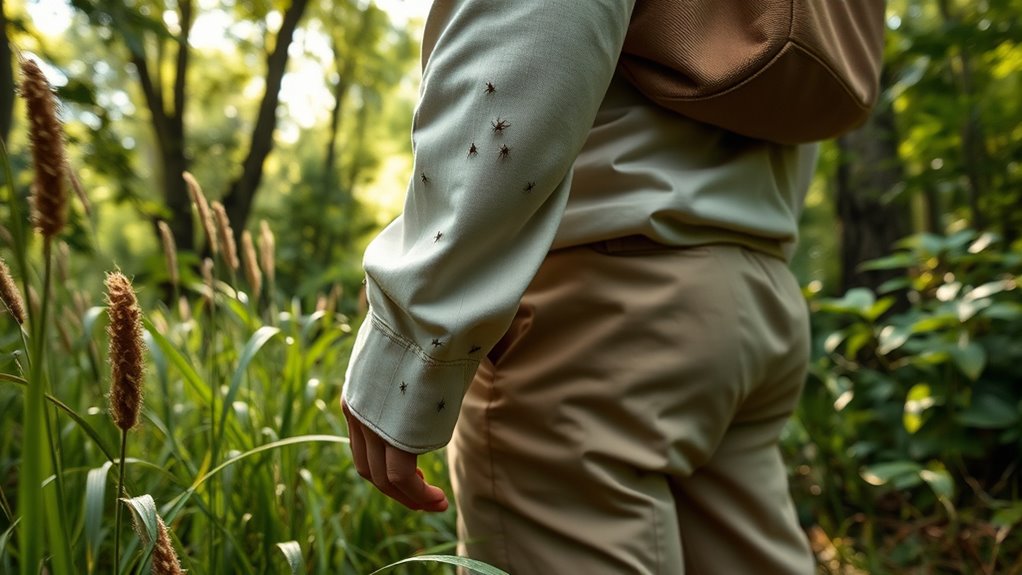

To effectively reduce your risk of tick bites, take proactive prevention measures when spending time outdoors. Wear tick-proof clothing, such as long sleeves, pants tucked into socks, and closed-toe shoes, to create a physical barrier against ticks. Applying outdoor repellents containing DEET or permethrin adds extra protection, especially in high-risk areas. Avoid tall grass, leaf litter, and shaded wooded spots where ticks thrive. After outdoor activities, thoroughly check your skin, clothing, and gear for ticks. Showering promptly can remove unattached ticks before they latch on. Staying vigilant and prepared helps keep you safe while enjoying nature. Understanding tick-borne diseases can further motivate you to follow these prevention strategies diligently. Incorporating proper equipment and clothing can also enhance your safety measures against tick-borne illnesses. Additionally, learning about essential oils for tick prevention may provide alternative natural repellents to consider.
The Role of Climate Change in Expanding Tick Habitats
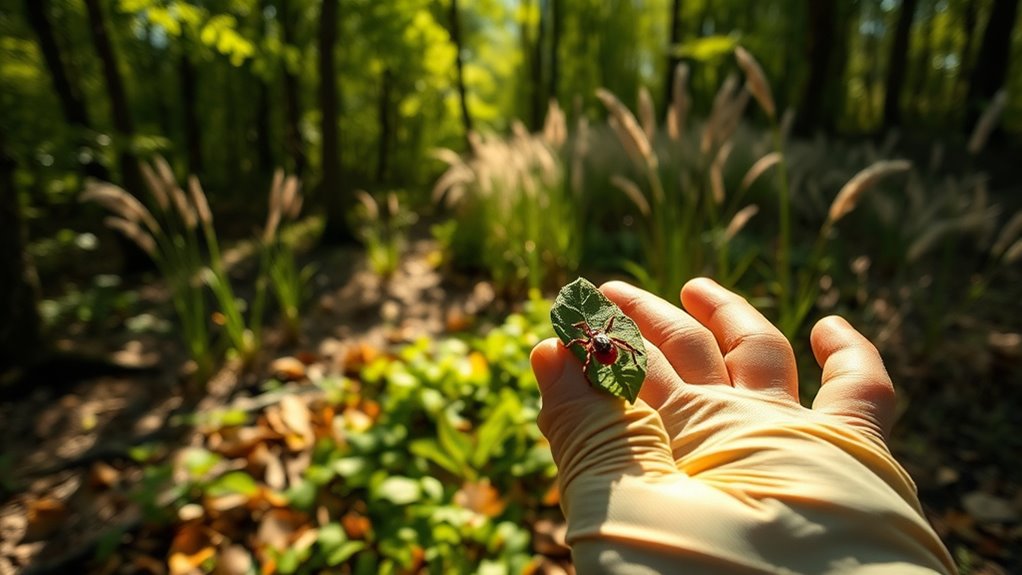

As climate patterns shift, the habitats suitable for ticks are also changing, leading to increased risks in areas once considered low-risk. Warmer temperatures and higher humidity enable ticks to thrive in new regions. Urban sprawl contributes by disturbing natural environments, pushing ticks into residential areas. This expansion makes it easier for ticks to encounter humans and pets. Additionally, climate change accelerates the spread of tick-borne diseases by creating more favorable conditions for ticks year-round. When considering vector-borne disease prevention, public awareness and proactive strategies become essential. To combat this, consider these strategies:
- Support vaccination programs that protect against tick-borne illnesses.
- Maintain clear yards to reduce tick-friendly habitats.
- Stay informed about changing climate zones and tick activity levels.
- Implement Necessary Cookies settings to ensure our website functions properly while you access relevant health information.
Furthermore, understanding the vector ecology helps in predicting and managing outbreaks effectively.
Advances in Research and Treatment for Tick-Borne Diseases
Recent advances in research have markedly improved our understanding of tick-borne diseases and opened new avenues for treatment. Researchers are now making significant progress in vaccine development, aiming to prevent infections before they occur. These efforts could lead to effective vaccines for diseases like Lyme disease and others transmitted by ticks. Additionally, diagnostic advancements have revolutionized how quickly and accurately we can identify infections. New testing methods allow for early detection, enabling prompt treatment and better outcomes. These innovations are essential, especially as tick-borne diseases become more prevalent. By combining vaccine development with improved diagnostics, healthcare providers can better protect individuals and reduce the disease burden. Staying informed about these advancements helps you understand the evolving landscape of tick-borne disease prevention and care. Emerging technologies continue to shape the future of disease management and patient outcomes. Furthermore, understanding tick biology and behavior enhances prevention strategies and risk assessment. Gaining knowledge about vector ecology can also aid in designing more effective control measures, including targeted interventions based on vector behavior patterns.
Community and Individual Actions to Reduce Risk

Reducing your risk of tick-borne diseases requires proactive steps at both the community and individual levels. Personal protection is crucial; always wear long sleeves and pants when outdoors, use EPA-approved insect repellents, and perform thorough tick checks after activities in grassy or wooded areas. Community awareness also plays a key role—support local efforts to control tick habitats, participate in awareness campaigns, and encourage neighbors to stay vigilant. Utilizing multi-factor authentication can also help minimize exposure to ticks. By combining these actions, you help lower the chances of tick bites and disease transmission. Staying informed about tick activity and sharing knowledge with others strengthens community defenses. Your efforts, along with community initiatives, create a safer environment for everyone, reducing the overall risk of tick-borne illnesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Can Ticks Survive Without Feeding?
Tick survival varies depending on species and environmental conditions. Without feeding, ticks can endure fasting durations ranging from several months to over a year. For example, some ticks can survive up to two years without a blood meal, especially in cooler, drier climates. This fasting duration highlights how resilient these parasites are, making it vital for you to check for ticks regularly after outdoor activities to prevent potential disease transmission.
Are There Any Vaccines Available for Tick-Borne Diseases?
Vaccination options for tick-borne diseases are limited, but some vaccines do exist. For example, there’s a Lyme disease vaccine available for dogs, though human vaccines are not widely accessible yet. Ongoing vaccine development aims to create effective options for humans, but it’s still in progress. You should stay informed about new vaccines and consider preventive measures, like using repellents and checking for ticks after outdoor activities.
What Types of Wildlife Contribute Most to Tick Populations?
Imagine the wild orchestra around you—certain wildlife dramatically shape tick populations. You should know that wildlife diversity, especially deer, rodents, and birds, contribute most to ticks’ spread. These animals often prefer specific tick habitat preferences, making them key players in maintaining and expanding tick habitats. Understanding which wildlife boosts tick numbers helps you take targeted actions, reducing your risk of tick-borne diseases.
Can Pets Act as Carriers of Tick-Borne Illnesses?
Pets can act as carriers of tick-borne illnesses, so pet transmission is a real concern. When your pets go outdoors, they might pick up ticks and bring them into your home, increasing carrier risks. Regularly checking your pets for ticks, using preventative treatments, and keeping your yard tick-free helps reduce this risk. Being proactive protects both your pets and your family from potential health issues.
How Effective Are Natural Remedies in Preventing Tick Bites?
Natural remedies can be surprisingly effective in preventing tick bites. You might think herbal repellents act like magic shields, and some, like citronella or eucalyptus oil, do offer protection. Dietary supplements such as garlic or vitamin B1 are believed to make your scent less appealing to ticks, though evidence is limited. While not foolproof, combining these methods can markedly lower your risk, making you feel safer outdoors.
Conclusion
As tick-borne diseases continue to rise, staying informed and proactive is essential. Did you know that the CDC reports a 200% increase in Lyme disease cases over the past decade? By understanding symptoms, practicing prevention, and supporting research, you can protect yourself and your community. Don’t wait—your actions today can make a real difference in reducing your risk and combating this growing health threat.